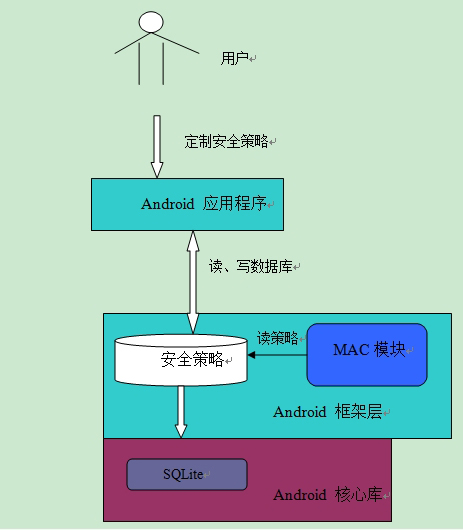
一个后端架构
2021-08-16
const http = require('http');
http.createServer((request, response) => {
// 请求的入口
}).listen(8080);
复制代码关于如何使用和对象来完成一个请求响应,大部分教程中都有提到。也可以查看Node的中文文档。这里就不详细介绍了。
处理静态文件
这里我们使用-,使用npm安装这个模块,在项目根目录下创建一个文件夹并放一些静态页面,创建一个.js文件:
const http = require('http');
const serveStatic = require('serve-static');
const publicPath = 'public';
const staticHandler = serveStatic(publicPath);
http.createServer((request, response) => {
staticHandler(request, response, () => {
// 失败回调
})
}).listen(8080);
复制代码以上代码是处理静态文件最简单的配置。需要注意的是()是异步操作。您可以通过使用 Node.js 运行 .js 来访问目录中的文件。
简单路由
要实现路由,首先要获取请求路径。 Node内置url模块的引入可以帮助我们解决这个问题
const url = require('url');
const http = require('http');
http.createServer((request, response) => {
const path = url.parse(request.url).pathname;
if (path === '/')
response.end('path is /');
else if (path === '/index')
response.end('path is /index');
else {
response.statusCode = 404;
response.end('Not Found');
}
}).listen(8080);
复制代码这是最简单的路由实现之一。需要注意的是,无论如何都必须调用.end()来终止请求,否则浏览器会一直等待对应的状态
在实际开发中,我们不会使用一系列的if...else来处理路由,一般创建一个路由映射表,加上静态文件处理:
const url = require('url');
const http = require('http');
const serveStatic = require('serve-static');
const publicPath = 'public';
const staticHandler = serveStatic(publicPath);
const map = new Map([
['/', response => {
response.end('path is /');
}],
['/index', response => {
response.end('path is /index');
}]
]);
http.createServer((request, response) => {
const path = url.parse(request.url).pathname;
if (map.has(path)) {
let handler = map.get(path);
handler(response);
} else
staticHandler(request, response, () => {
response.statusCode = 404;
response.end('Not Found');
});
}).listen(8080);
复制代码当前服务的处理逻辑是:先找到对应的路由,如果有,交给路由的回调处理,如果没有,在目录中寻找静态文件,返回404错误如果没有
结论
我还是为这个系列多写了几篇文章,但是我发现写的越多,对PHP越无所谓,所以打算放弃这个前缀,以后的文章会专注于Node的web发展
感谢阅读php开发笔记php开发笔记,欢迎指出文中错误,欢迎交流
接下来的几篇文章将介绍一个基于我最近在研究的开源框架的更复杂的后端架构。寻求关注和star